Contents
Mastars
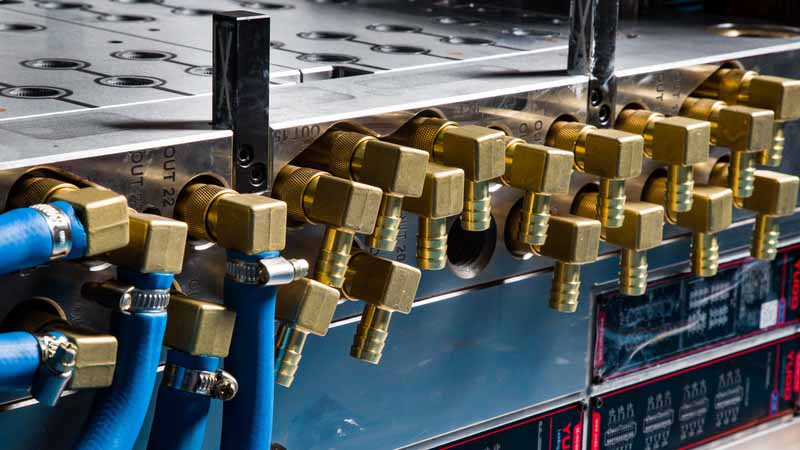
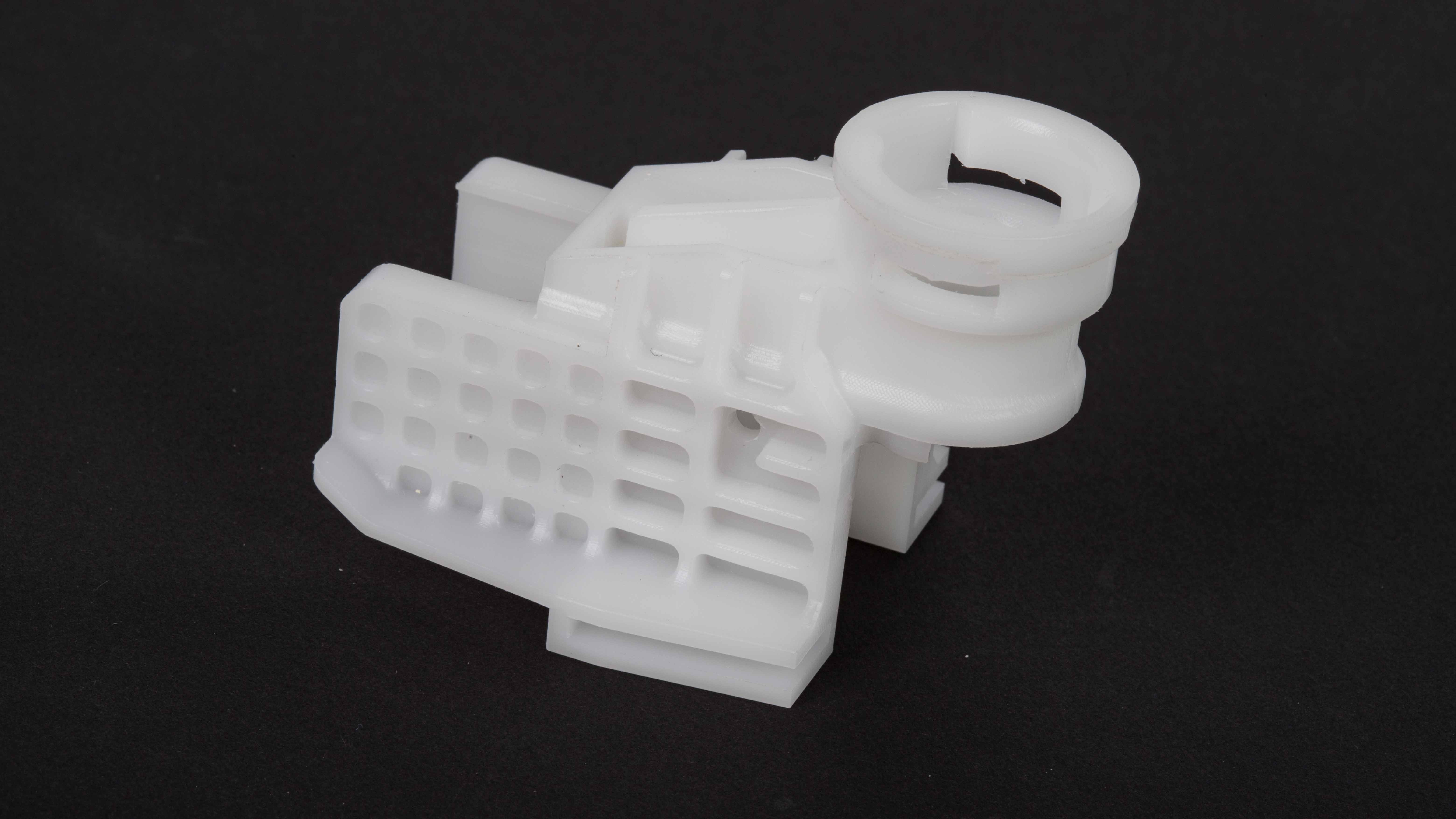
mold manufacturing
automobiles
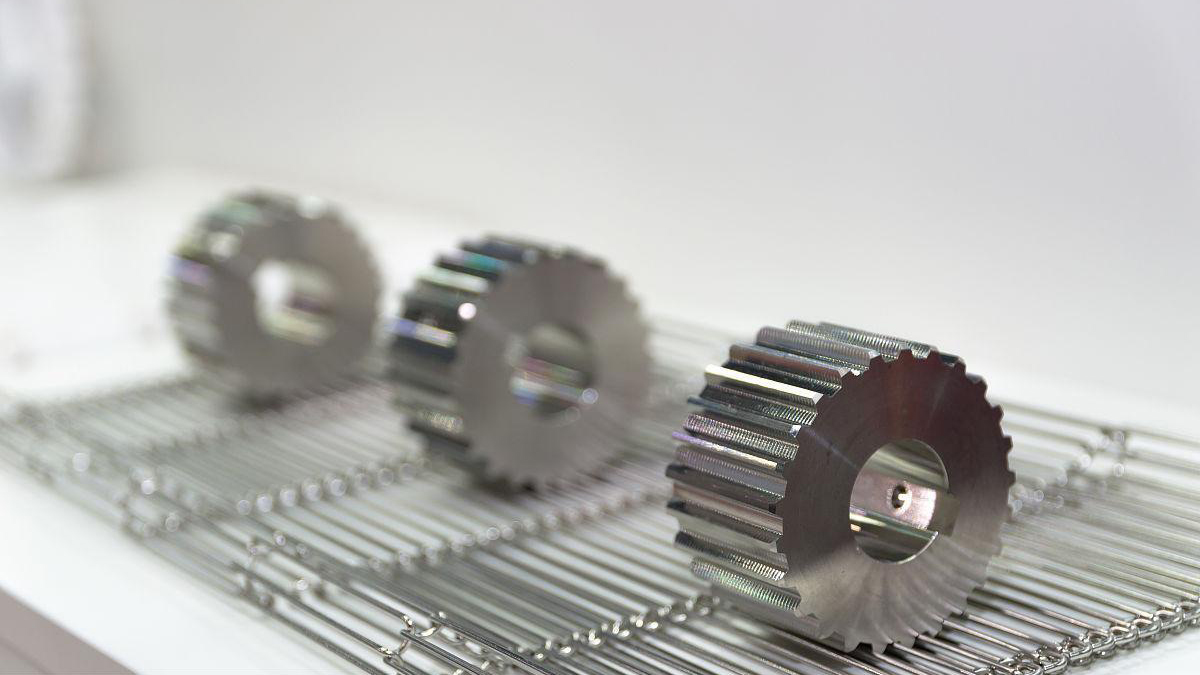
Mastars has more than 20 years of professional forging experience, focusing on
hot forging,
warm forging, cold forging, 3D forging technology for non-ferrous metals such as copper, aluminum alloy, stainless steel, etc., and has one-stop customized service of mold development,
mold manufacturing, product manufacturing and surface treatment. Supporting large-scale equipment: 4000 tons, 2500 tons, 800 tons, 630 tons, 400 tons
forging machines, 1000 tons 4D forging machines, 500 tons 3D forging machines,
CNC machining centers, punches, spark machines, electric discharge machines, grinders, etc. Perfect equipment and strong technical force have unique advantages in the development and manufacture of "high, precise and large" forgings.
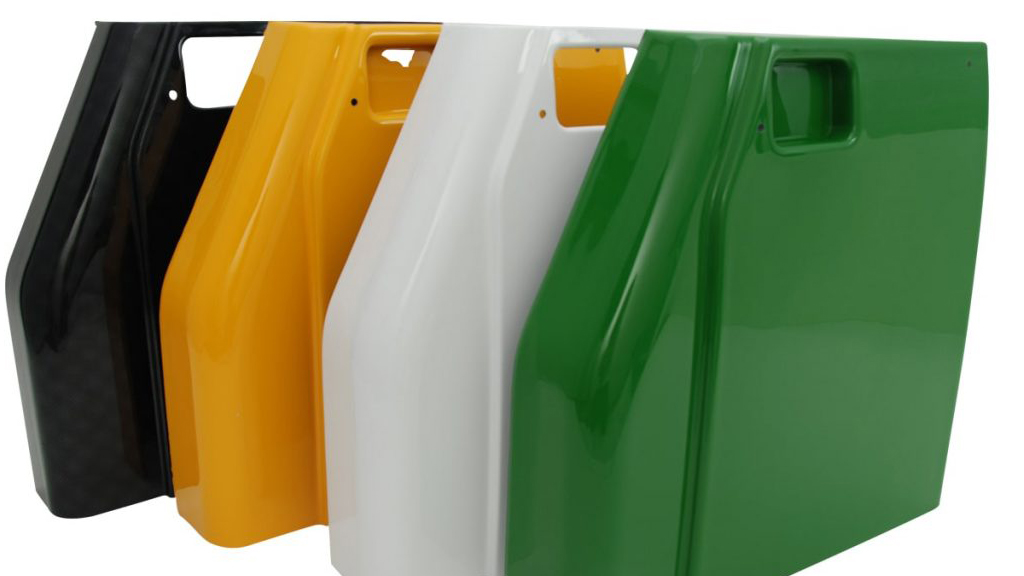
Products are widely used in
automobiles, electric vehicles,
motorcycles, bicycles, outdoor sports, military ships, aerospace and other industries. Forging equipment with a tonnage of 4000 tons can forge workpieces with an outer diameter of 500mm and a length of 1000mm. The forging precision can reach 0.1--0.2mm, and the machining dimensional accuracy tolerance is 0.01-0.05mm.
Forging (processing method)
Forging is a processing method that uses a forging machine to apply pressure on a metal blank and cause plastic deformation to obtain a forging with certain mechanical properties, certain shape and size. It is one of the two major components of forging (forging and stamping). Through forging, defects such as cast looseness produced by the metal during the smelting process can be eliminated, and the microstructure can be optimized. At the same time, due to the preservation of the complete metal streamline, the mechanical properties of forgings are generally better than those of castings of the same material. Forgings are mostly used for the important parts with high load and severe working conditions in related machinery, except for the simple plate, profile or welding parts that can be rolled.
Deformation temperature
Above 800 ℃ is hot forging; between 300 and 800 ℃ is called warm forging or semi-hot forging, and forging at room temperature is called cold forging.
Forgings used in most industries are hot forged. Warm forging and cold forging are mainly used for forging parts such as automobiles and general machinery, which can effectively save materials.
Forging materials
Forging materials are mainly carbon steel and alloy steel of various compositions, followed by aluminum, magnesium, copper, titanium and their alloys. The original state of the material is bar, ingot, metal powder and liquid metal.
Forgings compared to castings
Castings are metal forming objects obtained by various casting methods, that is, the smelted liquid metal is injected into the pre-prepared casting mold by pouring, injection, suction or other casting methods, and after cooling, it is subjected to falling sand, cleaning and post-processing to get an object of certain shape, size and performance.
Compared with castings, the microstructure and mechanical properties of metal can be improved after forging. Due to the deformation and recrystallization of the metal after the casting structure is deformed by the
forging method, the original coarse dendrites and columnar grains become an equiaxed recrystallized structure with finer grains and uniform axial recrystallization structure. The segregation, porosity, pores, slag inclusion and other phenomena of the metal are compacted and welded, and the structure becomes more compact, which improves the plasticity and mechanical properties of the metal.
The mechanical properties of castings are lower than those of forgings of the same material. In addition, the forging process can ensure the continuity of the metal fiber structure, so that the fiber structure of the forging is consistent with the shape of the forging, and the metal streamline is complete, which can ensure that the parts have good mechanical properties and long service life. Forgings produced by precision die forging, cold extrusion, warm extrusion and other processes are incomparable to castings.
The forging process builds a refined grain structure and improves the physical properties of the metal. In the practical use of parts, a proper design enables particle flow in the direction of the main pressure.
Importance
Forging production is one of the main processing methods for providing mechanical parts blanks in the machinery manufacturing industry. Generally, the important mechanical parts with high stress and high requirements are made by forging production method, such as steam turbine generator shafts, rotors, impellers, blades, guard rings, large hydraulic press columns, high pressure cylinders, rolling mill rolls, internal combustion engine crankshafts, connecting rods, gears, bearings, and artillery in the defense industry and other important parts are produced by forging.
Therefore, forging production is widely used in metallurgy, mining,
automobiles, tractors, harvesting machinery, petroleum, chemical industry, aviation, aerospace, weapons and other industrial sectors, even in daily life, forging production also has an important position.
In a sense, the annual output of forgings, the proportion of die forgings in the total output of forgings, the size and ownership of forging equipment and other indicators, to a certain extent, reflect the industrial level of a country.
Mastars Industries CO., LTD
www.mastars.com
Email: marketing@mastars.com
Tel: +86 755-88210690
Mobile: +86 181 0029 4997
Add: Building 6,Blue Sky Industrial Park, Ditang Road, Shajing Town, Shenzhen City, Guangdong, China